
|
 |
 |
Sea of Hypotheses |
| The 490 region and the 150 region get intimate
|
 The Closing Canyon
The Closing Canyon
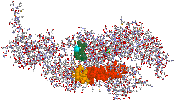
he "cleft" that forms the mouth of the whale has constituted a cornerstone of theories of contraction since its proposal by Rayment et al. Our genetic data may be pointing us to another rift in myosin that I will refer to as the Canyon. The region is at the "back of the head" of the whale (the two parts are 145-150, in green-blue and cyan, and the region around 494, in orange), and can be perceived as a canyon with a couple residues entering it from the sides. The genetic linkage that suggests an interaction across this region (implying the motor at some point has a shape in which the canyon is closed) is both strong and weak: several mutants in and around the Camshaft (N483S, Y494K and W501L) can be restored to function by a single change: E150K. While we have recovered this change at least 7 times, we have not found any other changes that have a restorative effect in any other residues between 125 and 175. Nonetheless, I think there are several reasons to consider a "partnership" between the 145-150 region and the 489-498 region of myosin. While proteins have many "kinds" of interactions that attract parts to one another, I think 150->490s involves the simplest: positively and negatively charged amino acids [(+) = K, R, (-) = D, E]. Examination of the sequences around E150K turns up a conserved pattern of charged residues: in myosin, the sequence 145-155 runs GRRRQK, where red indicates positively charged residues and blue negative. The region around position Y494 also contains a cluster of charges--the sequence 489-498 reads EQEEYLKEK. We know from other suppressor work that charge is important in this region--not only is the Y494K change a substitution of a positively charged lysine for an uncharged tyrosine, but it can be restored by converting the positively charged K496 to E. Interestingly, in the published structures, these residues are on the surface of the molecule--contacting water. There is no a priori reason why water cares if they are positively or negatively charged, but these positions bear the same charge in almost all myosins--as if they talk to something besides water at some point. The same is true for the 150 region. Thus I take the straightforward step of guessing that the 150 region "talks to" the 494 region. A picture showing how these regions appear in the chicken structure is shown (note that here and elsewhere, I am using Dicty #s to make things uniform; the actual # are a little different in the chicken structure even though the amino acids and their structural location are very very similar). The CamShaft is shown in redorange, while the positively charged residues of the 150 region are in salmon and the E150 position is shown in cyan. To highlight their close approach, residue Q149 is shown in purple and residue K496 in orange. We have also found other residues that might influence this proposed movement; they are shown in yellow, and the essential light chain (a small protein that actually forms an important part of the motor) is in purple. The P536 position is in blue for orientation. The "lighting" is from above, so the canyon between the 150 and 490s regions is dark where it's deep.


What do we intend to do about it?
en White is taking a two-pronged approach to assessing the potential interactions between the 150 region and 490 region of myosin. First, we are substituting sequences from other myosins at each region. Our logic is that if the two regions do directly interact, then each species will have complementary sequences at the two positions, BUT that having region 150 from one species and region 494 from another will give rise to an unmatched pair, creating a disfunctional motor. By seeing which combinations of region 150 and region 490 work, we hope to generate strong support for the direct interaction hypothesis.
n order to further characterize the two regions, Ben is also mutagenizing the charged residues in both regions. By characterizing the resulting mutants, we will learn what characteristics of each region are important for function. He will also test mutagenized region 150 for ability to suppress the Y494K and W501L mutations that are suppressed by the E150K mutation.

|
 The Closing Canyon
The Closing Canyon




